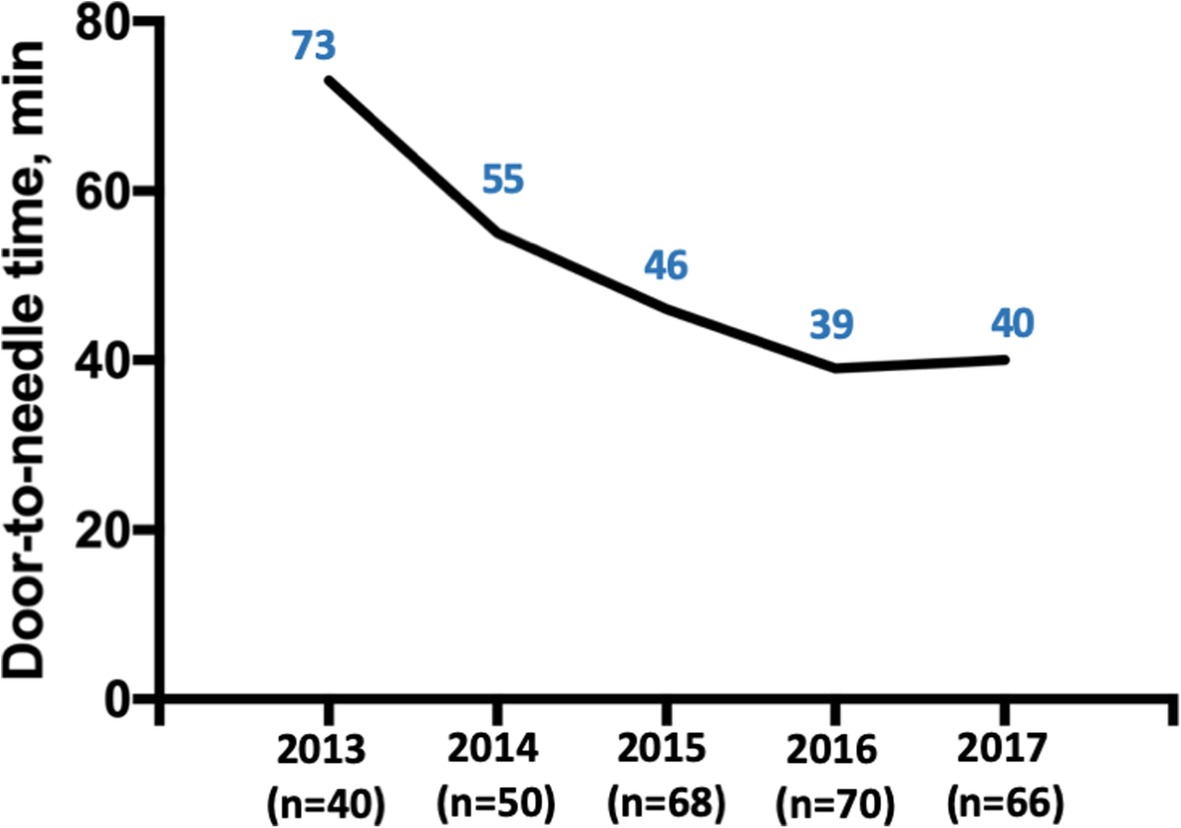
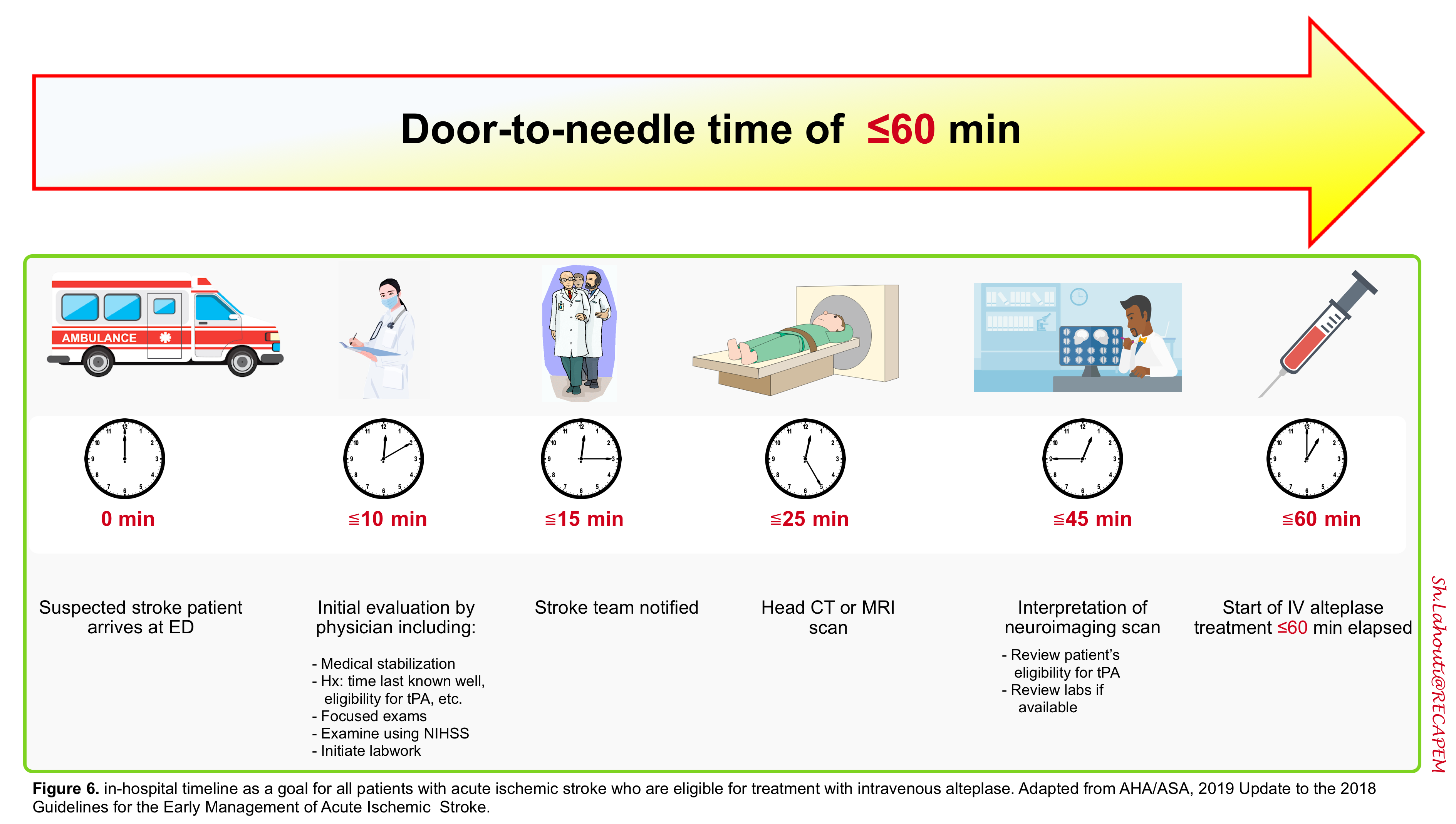
Frontiers | Helsinki Stroke Model Is Transferrable With “Real-World” Resources and Reduced Stroke Thrombolysis Delay to 34 min in Christchurch

ST-Segment–Elevation Myocardial Infarction Treatment and the Seductive Lure of Observational Analyses | Circulation

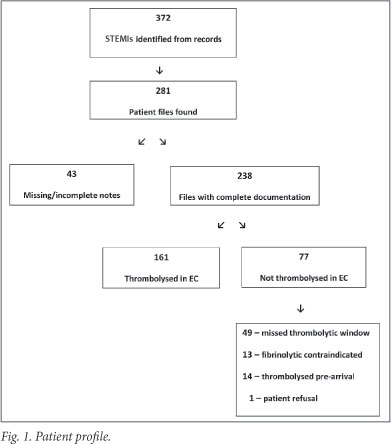
Cureus | Impact of Delayed Pain to Needle and Variable Door to Needle Time On In-Hospital Complications in Patients With ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Who Underwent Thrombolysis: A Single-Center Experience

Thrombolysis: Improving door-to-needle times for ischemic stroke treatment – A narrative review - Noreen Kamal, Eric E Smith, Thomas Jeerakathil, Michael D Hill, 2018
Evaluation of a multicomponent intervention to shorten thrombolytic door-to-needle time in stroke patients in China (MISSION): A cluster-randomized controlled trial | PLOS Medicine
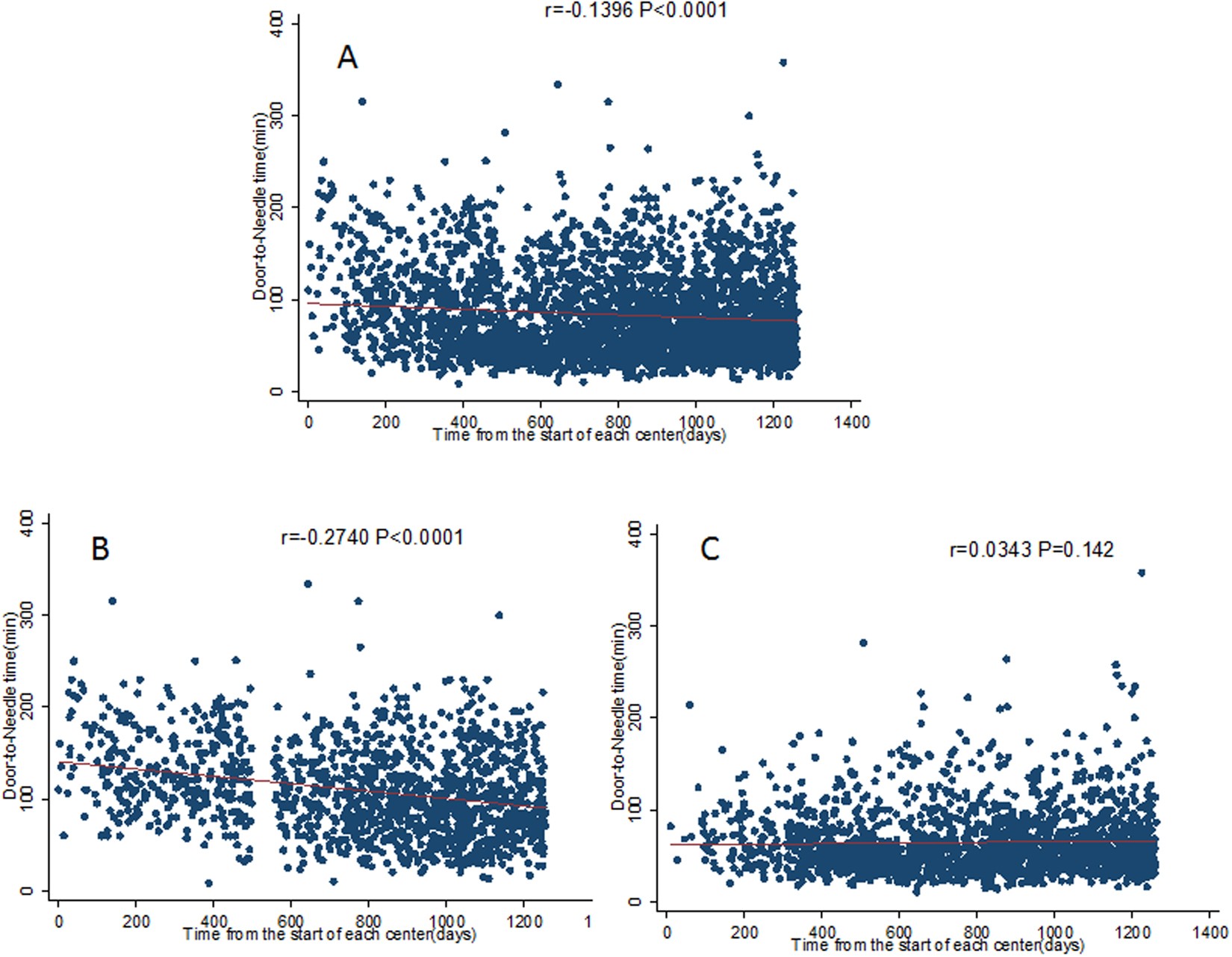
Positive impact of the participation in the ENCHANTED trial in reducing Door -to-Needle Time | Scientific Reports

Door-to-Needle (DTN) Times for tPA and Clinical Outcomes in Acute Ischemic Stroke Before and After a Quality Improvement Initiative | tctmd.com
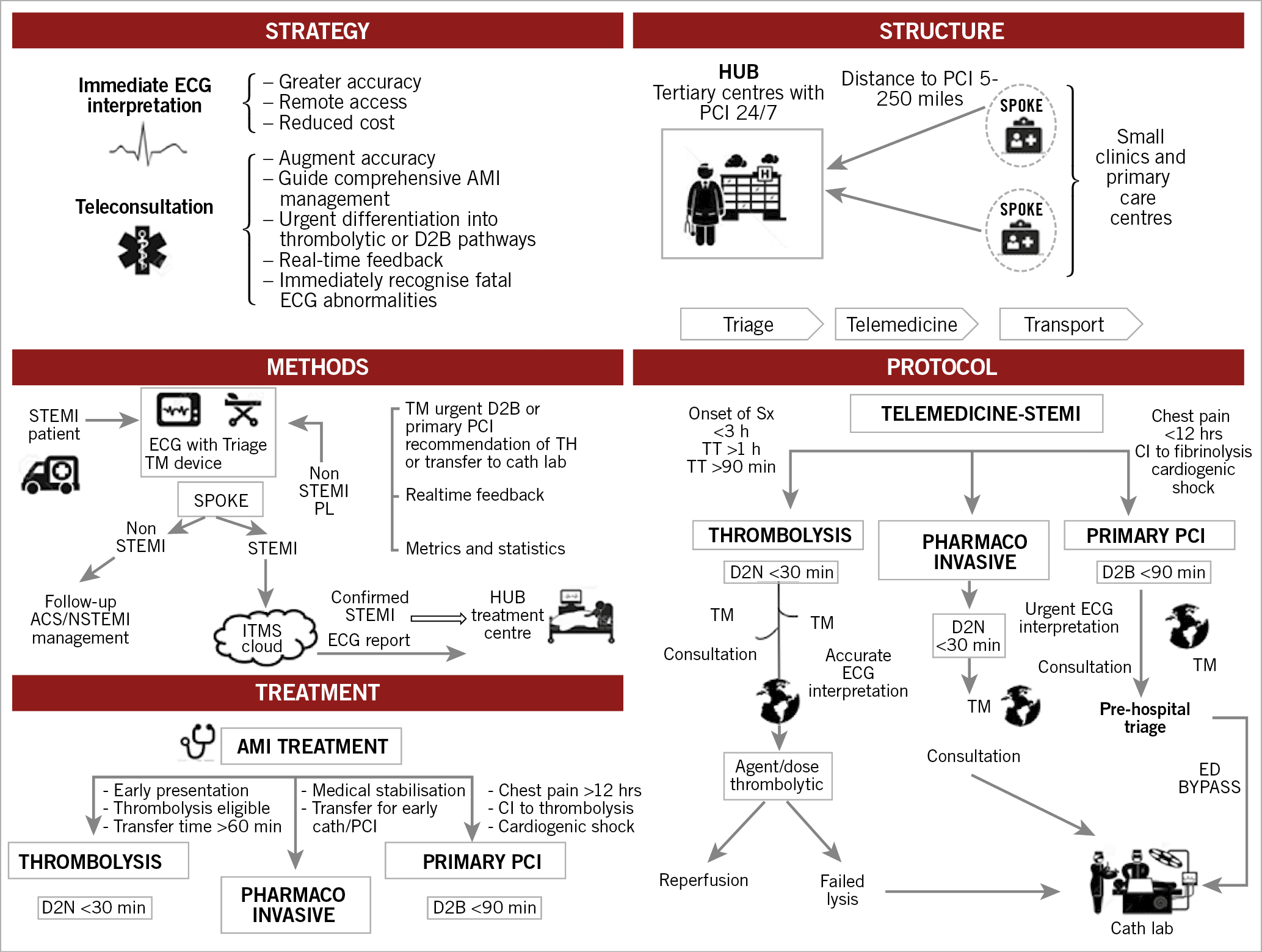
Impact of a telemedicine-guided, population-based, STEMI network on reperfusion strategy, efficiency, and outcomes – AsiaIntervention

Recommendation to Develop Strategies to Increase the Number of ST-Segment–Elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients With Timely Access to Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention | Circulation

Tenecteplase Improves Door‐to‐Needle Time in Real‐World Acute Stroke Treatment | Stroke: Vascular and Interventional Neurology

Quality improvement project to improve patient outcomes by reducing door to CT and door to needle time and increasing appropriate referrals for endovascular thrombectomy. | BMJ Open Quality